Your content team just published a comprehensive 5,000-word guide backed by original research, expert interviews, and detailed analysis. It’s objectively better than the Wikipedia entry on the same topic, more current, thorough, and better written.
Yet when users ask ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google’s AI Mode about your topic, they cite Wikipedia. Not you.
This isn’t an accident, and it’s not about quality. Wikipedia dominates AI citations because of structural trust advantages that have nothing to do with having the “best” content.
Key Findings:
- AI prioritizes Wikipedia’s entity authority over individual page superiority; build broad domain signals through neutral, authoritative coverage first.
- Commercial content triggers AI bias detectors: adopt an objective style with inline citations to mimic Wikipedia’s verification loops.
- Wikipedia’s reference structure creates AI-recognized credibility; add 5-10 authoritative sources per section, not just links.
- Target “how-to implement,” product comparisons, and niche recommendations where Wikipedia lacks depth: commercial intent spaces.
- AI citations build brand association without clicks; track share-of-voice across ChatGPT/Perplexity vs. Wikipedia, not sessions.
The Numbers Don’t Lie: Wikipedia’s Citation Dominance
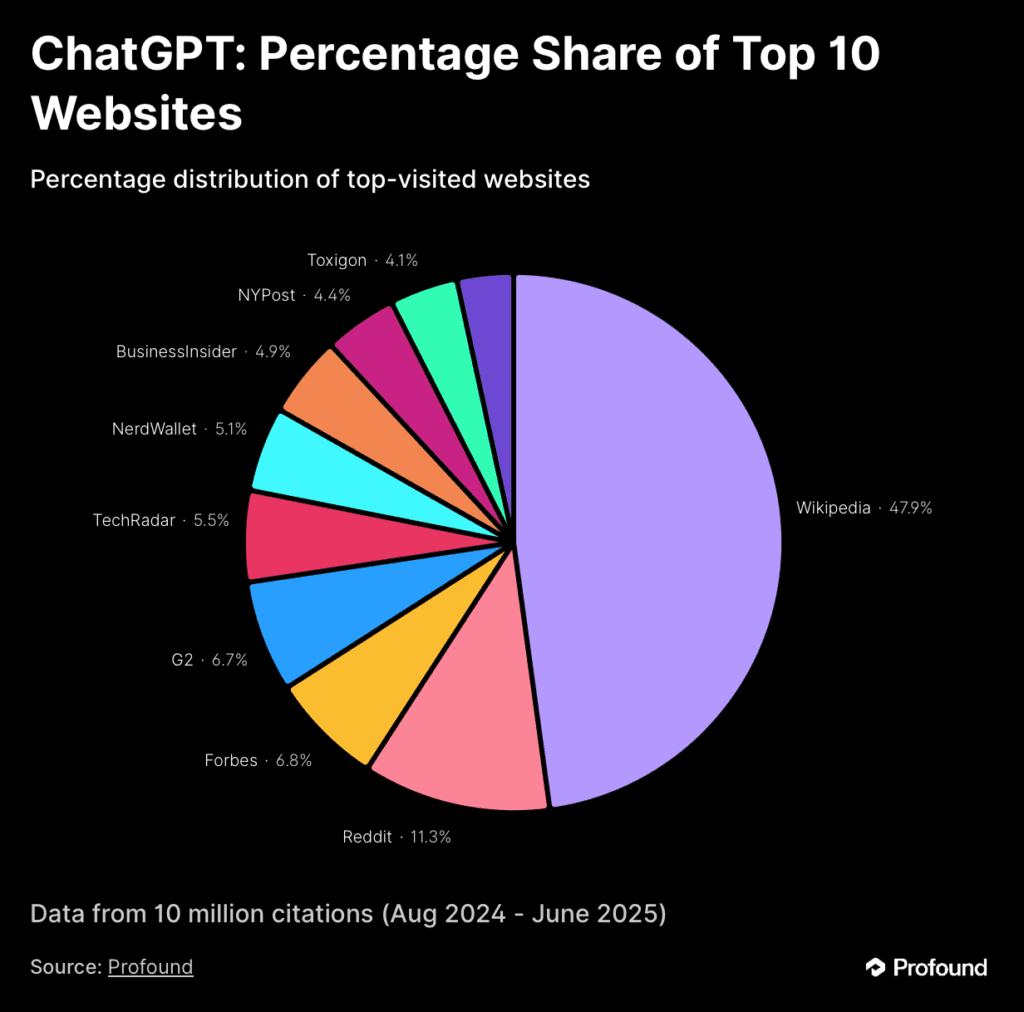
Recent analysis examining 680 million AI citations across major platforms reveals a pattern that should concern every content creator and marketer. Within ChatGPT’s top 10 most-cited sources, Wikipedia accounts for nearly half at 47.9% of citations among these leading sources.
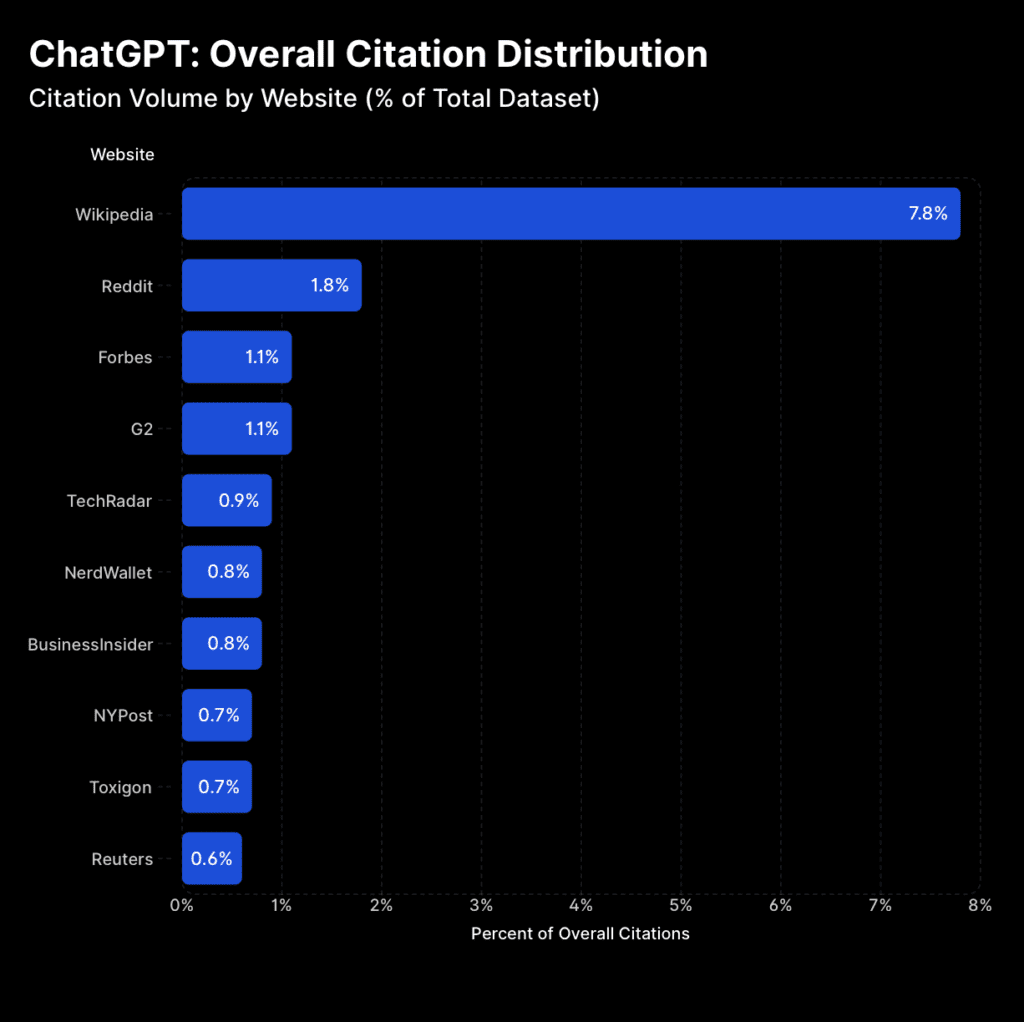
Even more striking: Wikipedia represents 7.8% of ChatGPT’s total citations, making it the platform’s single most cited source.
The dominance extends beyond a single platform. Research analyzing how different AI engines generate and cite answers shows that Wikipedia serves as a foundational source across multiple systems, though platforms weigh it differently.
For publishers and brands creating high-quality content, these statistics present an uncomfortable reality:
- The market isn’t rewarding content quality in AI search the way it did in traditional search engines.
- The question “Is Wikipedia reliable?” matters less to AI engines than the structural signals Wikipedia sends about trustworthiness.
Why AI Engines Default to Wikipedia
| Wikipedia’s AI Trust Advantage | Why It Wins | Implication for Brands |
| Entity Authority | Domain-level trust for all topics; AI trusts Wikipedia automatically. | Prove domain trustworthiness first, not just individual pages. |
| Neutral Tone | Objective style avoids bias detectors AI uses to filter promotional content. | Write neutrally, even for commercial topics, to pass trust filters. |
| Citation Density | Inline refs create verification loops that AI recognizes as vetted content. | Match Wikipedia’s reference density and structure for credibility. |
| Network Effect | Massive scale in training data makes Wikipedia’s format the “good source” template. | Build comprehensive coverage AI training learned to prefer. |
The Structural Advantage You Can’t Copy
You probably can’t replicate Wikipedia’s structural advantages, and you should not even try. Wikipedia AI dominance isn’t built on tactics you can copy. It’s the differences in how the platform operates.
Wikipedia has no commercial incentive.
- It’s maintained by thousands of volunteer editors who follow strict neutrality guidelines.
- It’s been accumulating citations, links, and trust signals for over two decades.
- It’s structured as a nonprofit educational resource.
Most importantly, every major AI platform used Wikipedia as training data, embedding its patterns deep into their models.
These aren’t surface-level optimizations. They’re core identity factors that brands cannot match. The scale AI Wikipedia trained on means even creating better individual articles won’t overcome the systemic trust gap.
What This Means for Content Strategy
3 Ways to Win AI Citations (Without Fighting Wikipedia)
- Skip encyclopedic queries: Wikipedia owns “What is [topic]?“; target commercial searches, niche how-tos, and fresh recommendations.
- Build Wikipedia-style trust: Cite authorities neutrally, cover topics deeply, and engage on Reddit/professional forums.
- Dominate commercial spaces: Product comparisons and implementation guides, where Wikipedia can’t compete.
Recent data shows that Wikipedia traffic is declining even as its influence on AI answers grows. This creates a fascinating dynamic: the platform training all AI systems isn’t benefiting from that influence in traditional traffic metrics.
Users receive Wikipedia-sourced information without even visiting the site.
This should concern every publisher. If Wikipedia, the most cited source in AI search, isn’t converting citations into traffic, what does that mean for brands that do earn citations?
The answer is that AI citations might not drive traffic the way traditional search rankings did. The value may be in brand awareness and trust-building rather than click-through rates.
For marketers trying to optimize content for AI search, this requires a mindset shift. Success might look less like traffic spikes and more like a consistent presence across AI answers in your category, even without attribution that drives clicks.
The goal becomes training AI systems to associate your brand with specific topics and queries, building the same type of domain-level trust that makes Wikipedia the default choice.
Wikipedia beats your content in AI answers not because it’s always better, but because it offers AI systems something they value more than quality: verification safety, neutral tone, dense citations, and two decades of accumulated trust signals. These advantages are structural, not tactical, and cannot be easily replicated by commercial publishers.
If you want to build trust by getting your brand cited on LLM-powered search, book a call with us.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why does Wikipedia beat my superior content?
Domain-level trust, neutral tone, citation density, and structural edges AI models learned from training data.
2. Can brands copy Wikipedia’s advantages?
No, volunteer scale, 20+ years of trust, nonprofit status can’t be replicated.
3. What queries should I target?
Skip “What is [topic]?“; chase commercial searches, niche how-tos, fresh recommendations.
4. Do AI citations drive traffic?
Rarely, Wikipedia traffic drops despite AI dominance; value is brand trust.
5. How do I build AI trust?
Neutral writing, dense citations, deep coverage, Reddit engagement, mimic signals, not structure.