For the first time since 2015, bots have overtaken humans online. According to Imperva’s 2025 Bad Bot Report, automated systems now control 51% of all internet traffic. More concerning: bad bots, those designed for data theft, fraud, and disruption, account for 37% of all traffic, representing a sixth consecutive year of growth.
This is a business crisis. AI has supercharged bot capabilities, enabling sophisticated attacks that were once the domain of well-resourced cybercriminal organizations to be executed by anyone with basic technical skills. DataDome reports that AI-powered bot requests have quadrupled to 10% of all web traffic, while Imperva notes its systems block over 2 million attacks daily, a number that continues to climb.
The message is clear: The time to fight back is now.
Key Takeaways:
- Bots overtook humans, controlling 51% of internet traffic for the first time since 2015, per Imperva’s 2025 Bad Bot Report.
- Bad bots, used for theft and fraud, hit 37% of traffic, a sixth year of growth, with simple AI bots now 45% of attacks.
- AI-powered credential stuffing caused a 54% rise in account takeovers since 2022, with 14% of logins malicious.
- AI bot requests quadrupled to 10% of traffic (DataDome), targeting APIs (44% of advanced bots) for scraping and fraud.
- Humans account for 49% of traffic, shifting the internet to a machine-dominated field
The 2024 Bot Breakdown
Bad Bots: 37% of All Traffic
Bad bots engage in malicious activities like web scraping, credential stuffing, payment fraud, inventory hoarding, and API abuse. The 37% figure (as above) is especially alarming because simple bots using basic automation now make up 45% of bad bot traffic, up sharply from previous years. This surge is driven by AI tools that allow less skilled attackers to launch high-volume campaigns with minimal technical expertise.
Good Bots: 14% of Traffic
Not all automated traffic is malicious. Good bots serve essential internet functions, including search engine crawlers that enable discovery, monitoring services that ensure uptime and performance, feed fetchers that aggregate content legitimately, and authorized API clients that power integrations.
However, the challenge lies in distinguishing good bots from bad ones masquerading as legitimate crawlers, a task made exponentially harder by AI-powered evasion techniques.
Humans: 49% of Traffic
For the first time in a decade, actual human users represent less than half of internet traffic. This minority status has profound implications for how businesses design security, allocate infrastructure resources, and understand their analytics data. It represents crossing a psychological threshold: the internet is now primarily a machine-to-machine field where humans are, statistically speaking, the minority participants.
AI: Attackers’ New Weapon
Credential Stuffing Gets Smarter
AI-powered credential stuffing drove a 54% surge in account takeover (ATO) attempts since 2022, with Imperva reporting 14% of all logins now malicious. Unlike simple scripts testing stolen credentials, AI optimizes timing, rotates proxies intelligently, mimics human behavior, and targets high-value accounts. These attacks evade traditional defenses, achieving profitable success rates despite sophistication.
Scraping Shifts from Noise to Revenue Risk
Kasada’s Q2 2025 analysis revealed a critical evolution: AI-powered scraping has shifted from being primarily a nuisance to representing direct revenue risk. Modern scrapers extract:
- Pricing data (competitor undercutting)
- Inventory info (hoarding/resale)
- Proprietary algorithms/business logic
- Customer data (phishing/competitive intel)
DataDome’s finding that AI bot requests quadrupled to 10% of all traffic reflects this evolution. These are sophisticated operations using AI to identify valuable data, evade detection through behavioral mimicry, and extract information at scale.
Evasion Techniques Become Adaptive
The most concerning AI impact is adaptability. AI-powered bots learn from blocking attempts, adjusting their behavior in real-time to evade detection. They analyze which patterns trigger security responses and modify approaches accordingly, creating an arms race where static defenses become obsolete quickly.
This adaptive capability means businesses can no longer rely on one-time security configurations. Bot defense now requires continuous evolution, matching the pace of AI-driven evasion, a resource-intensive proposition that smaller organizations struggle to maintain.
APIs: The Vulnerable Frontier
Why APIs Are Targeted
APIs represent the “keys to the kingdom” for modern applications, providing direct access to business logic without the need to navigate user interfaces. According to Imperva’s analysis, the breakdown of API-focused attacks reveals clear priorities:
- Attackers extract product catalogs, pricing information, user profiles, and proprietary datasets through automated API calls that appear legitimate but occur at volumes and patterns indicating malicious intent.
- Bad bots test stolen credit cards, exploit pricing logic vulnerabilities, and manipulate transaction processes through direct API manipulation that bypasses front-end validations.
- Credential stuffing targets authentication endpoints directly, attempting thousands of login combinations without the rate limitations that browser-based attacks might encounter.
The API Defense Gap
The reason APIs are disproportionately vulnerable is architectural. Traditional web application firewalls (WAFs) focus on protecting rendered pages and form submissions; they’re designed around human interaction patterns. APIs, by contrast, are built for machine-to-machine communication, making it harder to distinguish legitimate automated traffic from malicious bots.
Many organizations deploy APIs without equivalent security controls to their public-facing websites, creating a “soft underbelly” that sophisticated attackers specifically target. The 44% concentration of advanced bots on APIs reflects attackers’ understanding of this vulnerability gap.
10-Point Protection Framework
| # | Step | Key Action | Benefit |
| 1 | Risk Identification | Map high-value endpoints: auth/logins, APIs with sensitive data/business logic, payments, inventory, user profiles | Focuses defense on revenue-critical assets |
| 2 | Vulnerability Reduction | Patch APIs, remove unnecessary endpoints, enforce auth/rate limiting, follow OWASP API Top 10 | Prevention > detection; closes exploit avenues |
| 3 | User-Agent Blocking | Blacklist bot frameworks, scraping tools, and known attack UA strings | Stops ~60% simple/high-volume bots |
| 4 | Proxy Management | Detect data center IPs, TOR nodes, rapid IP rotation; behavioral analysis for residential proxies | Counters IP evasion tactics |
| 5 | Automation Detection | Analyze mouse/keyboard dynamics, timing patterns, and session scripting via ML | Flags AI bots mimicking humans |
| 6 | Traffic Analysis | Baseline request volumes, geo distribution, user journeys, API patterns | Anomalies trigger bot alerts |
| 7 | Real-Time Monitoring | 24/7 alerts for login spikes, data access anomalies, API abuse | Matches 2M daily attack volume |
| 8 | MFA Enforcement | Require secondary factors on all auth endpoints | Cuts ATO by ~80% vs. credential stuffing |
| 9 | Bot Protection Solutions | Deploy Imperva, DataDome, Kasada, PerimeterX, Cloudflare | Advanced ML/biometrics > in-house builds |
| 10 | Strategic Development | Prioritize e-commerce checkout, registration, payments, mobile/partner APIs | Max ROI with limited resources |
Protection Framework Summary
| Framework Layer | Key Action | Impact |
| Prevention | User-Agent/Proxy blocks | Stops 60% basic bots |
| Detection | Behavioral analysis | Catches AI evasion |
| Response | Real-time + MFA | Reduces ATO by 80% |
The statistics are unambiguous: bots now control 51% of internet traffic, with bad bots representing 37% a sixth consecutive year of growth. AI has transformed bot capabilities from simple automation to sophisticated attacks that adapt in real-time, quadrupling AI bot requests to 10% of traffic and driving a 54% surge in account takeover attempts.
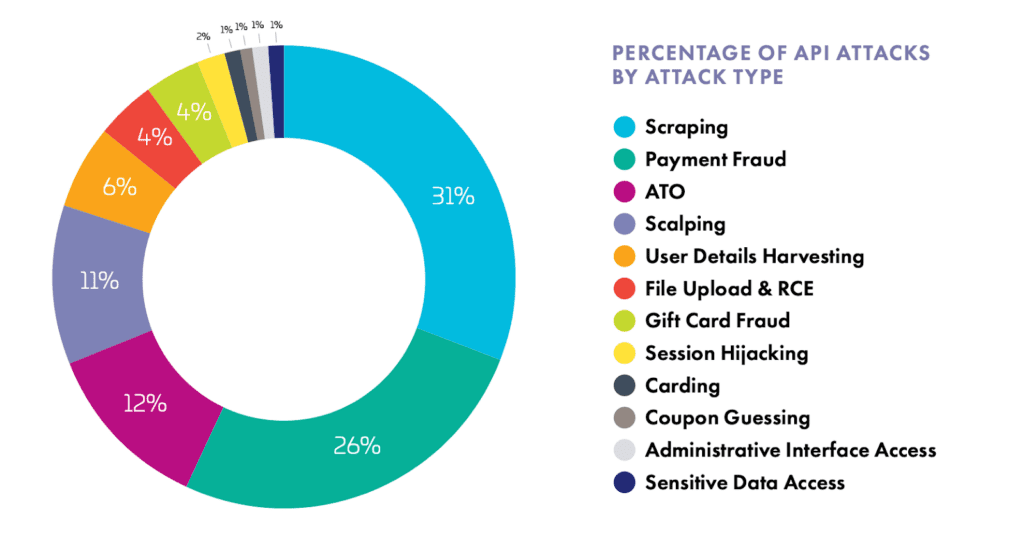
APIs have become the most vulnerable frontier, with 44% of advanced bots targeting these endpoints for data scraping (31%), payment fraud (26%), and account takeover (12%). Traditional defenses designed for human-facing applications leave APIs dangerously exposed.
The 10-point protection framework provides a systematic approach: identify risks, reduce vulnerabilities, block known threats, detect evasion, analyze patterns, monitor continuously, enforce MFA, deploy specialized solutions, and prioritize strategically. With Imperva blocking over 2 million attacks daily, the threat volume demands proactive, comprehensive defense, not reactive, piecemeal responses.
For businesses, the imperative is clear: audit your APIs and authentication systems today. Map where bots could inflict maximum damage. Implement layered defenses prioritizing revenue-critical paths. The bot problem is here, representing the majority of internet traffic and growing more sophisticated daily.
In an internet where bots have overtaken humans, remaining secure requires treating bot defense not as an IT issue but as a fundamental business imperative. The attackers are already using AI. The question is whether your defenses are keeping pace.
If you found this blog helpful, you’ll want to learn about AI crawlers.








